Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Gregorian and Julian Calendars
Related Articles: Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Gregorian and Julian Calendars
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Gregorian and Julian Calendars. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Gregorian and Julian Calendars

The passage of time is a fundamental aspect of human experience, and its accurate measurement has been a constant pursuit. Throughout history, various calendar systems have emerged, each with its own unique structure and rationale. Two prominent calendars, the Gregorian and Julian, have played significant roles in shaping our understanding of time and its implications.
The Julian Calendar: A Legacy of Caesar
The Julian calendar, named after Julius Caesar, originated in 45 BCE as a reform of the Roman calendar. It introduced a leap year every four years to align the calendar with the solar year, which is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one orbit around the sun. This leap year mechanism aimed to maintain the calendar’s synchronization with the seasons, preventing the gradual drift that occurred with the earlier Roman calendar.
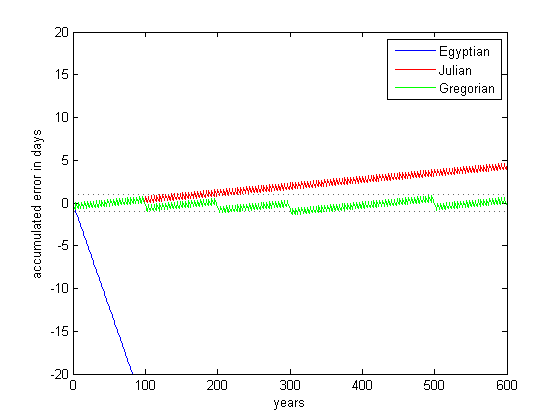
The Julian calendar, however, had a subtle flaw: it overestimated the length of the solar year by approximately 11 minutes and 14 seconds. This seemingly insignificant discrepancy accumulated over time, causing the calendar to gradually drift out of sync with the actual solar year. By the 16th century, this drift amounted to a significant difference of about 10 days, impacting the accuracy of the calendar’s alignment with the seasons.
The Gregorian Reform: A New Era in Timekeeping
Recognizing the growing discrepancy between the Julian calendar and the solar year, Pope Gregory XIII implemented a reform in 1582, resulting in the Gregorian calendar. This reform aimed to correct the Julian calendar’s drift and establish a more accurate system for timekeeping.
The Gregorian calendar addressed the Julian calendar’s flaw by adopting a more precise leap year system. It eliminated three leap years every four centuries, resulting in a more accurate alignment with the solar year. The Gregorian calendar also introduced a specific rule regarding century years: a century year is a leap year only if it is divisible by 400. For example, 1600 was a leap year, but 1700, 1800, and 1900 were not.
The Transition and its Impact
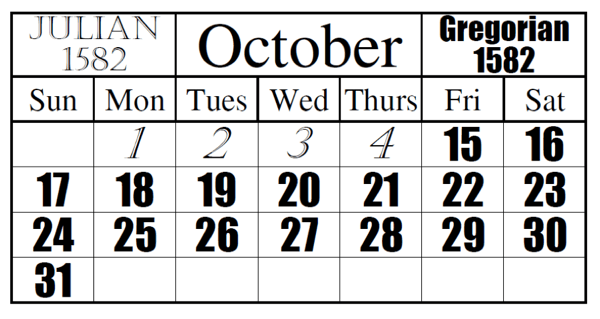
The transition from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar was not immediate and faced resistance in some regions. Catholic countries adopted the Gregorian calendar relatively quickly, while Protestant countries, notably England and its colonies, continued to use the Julian calendar for a significant period. This difference in calendar systems led to a discrepancy in dates between countries, creating confusion and potential complications in communication and record-keeping.
Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Difference
The Gregorian calendar is the standard calendar used in most parts of the world today. It is the calendar used for official purposes, including government, business, and scientific applications. The Julian calendar, while no longer the primary calendar in most regions, remains relevant in specific contexts, particularly in historical research and religious observances.
The difference between the two calendars is primarily the leap year system. The Julian calendar uses a leap year every four years, while the Gregorian calendar has a more refined system that eliminates three leap years every four centuries. This difference in leap year calculations leads to a gradual drift between the two calendars, resulting in a date difference that has accumulated over the centuries.
The Date Difference: A Historical Perspective
The date difference between the Gregorian and Julian calendars has been steadily increasing since the Gregorian reform in 1582. This difference is currently 13 days, meaning that a date on the Julian calendar is 13 days earlier than the corresponding date on the Gregorian calendar. For example, January 1st on the Julian calendar corresponds to January 14th on the Gregorian calendar.
Beyond the Calendar: The Importance of Historical Context
Understanding the difference between the Gregorian and Julian calendars is crucial for historical research and analysis. When studying historical events, it is essential to consider the calendar system used during that period to accurately interpret dates and timeframes. This is particularly important when dealing with events that occurred before the widespread adoption of the Gregorian calendar.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How do I convert a date from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar?
A: To convert a date from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar, you need to consider the date difference, which is currently 13 days. Add 13 days to the Julian calendar date to obtain the corresponding Gregorian calendar date. For example, January 1st on the Julian calendar corresponds to January 14th on the Gregorian calendar.
Q: Why is the Julian calendar still used in some contexts?
A: The Julian calendar remains relevant in specific contexts, primarily due to historical and religious reasons. Some religious groups, such as the Eastern Orthodox Church, continue to use the Julian calendar for religious observances. Historical research also utilizes the Julian calendar to accurately interpret dates and timeframes in historical documents.
Q: What are some examples of historical events where the calendar difference is significant?
A: The calendar difference is significant in historical events such as the Russian Revolution (1917), which occurred in January on the Julian calendar but in February on the Gregorian calendar. Similarly, the Gregorian calendar was adopted in Britain in 1752, resulting in a date difference that impacted the recording of historical events during that period.
Tips for Navigating the Temporal Divide
- Be mindful of the calendar system used: When researching historical events, always note the calendar system used in the source material.
- Consider the date difference: When comparing dates from different calendar systems, account for the date difference between the Julian and Gregorian calendars.
- Consult reliable resources: If you are unsure about the calendar system used in a particular context, consult reliable historical resources or experts.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Timekeeping
The Gregorian and Julian calendars represent two significant milestones in the evolution of timekeeping. While the Julian calendar was a significant advancement in its time, its inherent flaw led to the development of the more accurate Gregorian calendar. The Gregorian calendar remains the standard calendar used in most parts of the world today, serving as a testament to the ongoing pursuit of precision in our understanding of time. Understanding the differences between these two calendars provides valuable insights into the historical evolution of timekeeping and its impact on our understanding of the past.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Temporal Divide: Understanding the Gregorian and Julian Calendars. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!