Navigating the Market: Understanding the Economic Calendar
Related Articles: Navigating the Market: Understanding the Economic Calendar
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Market: Understanding the Economic Calendar. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Market: Understanding the Economic Calendar

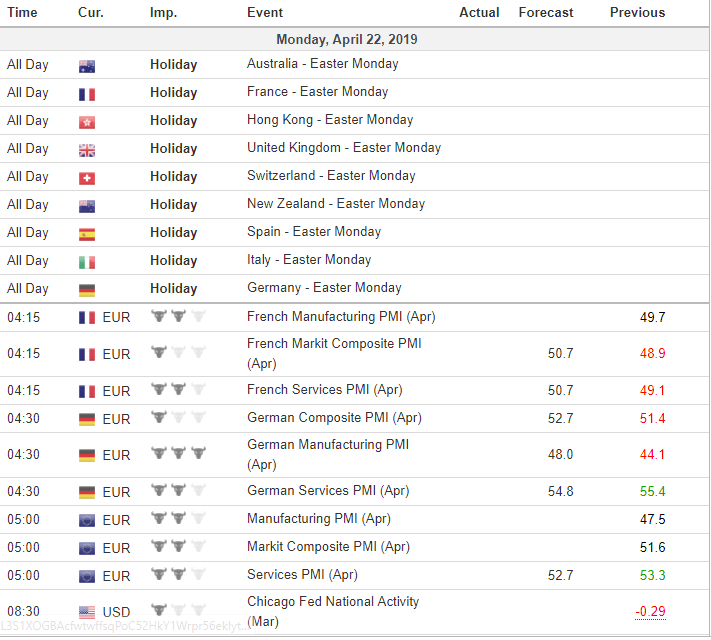
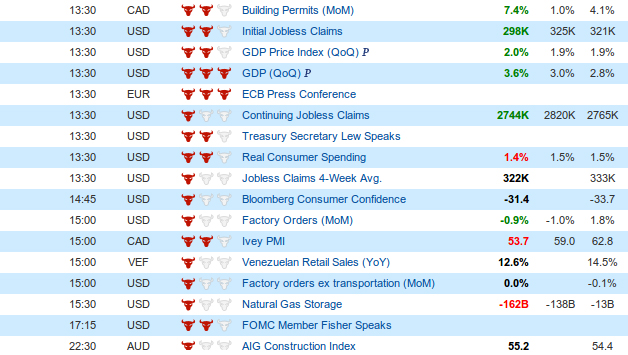
The stock market, a dynamic and often volatile ecosystem, is driven by a complex interplay of factors. Among these, economic data releases play a pivotal role, influencing investor sentiment and market direction. The economic calendar, a comprehensive guide to upcoming economic data releases, serves as an invaluable tool for navigating this complex landscape.
Decoding the Economic Calendar: A Guide to Key Data Points
The economic calendar is a meticulously curated schedule that outlines the release dates and times of various economic indicators. These indicators, ranging from inflation reports and unemployment figures to manufacturing data and interest rate decisions, provide crucial insights into the health of the economy.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the most significant data points featured on the economic calendar:
1. Inflation Reports:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This measures the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): This tracks the average change in prices received by domestic producers for their output.
- Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index: This is the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, reflecting changes in prices for goods and services purchased by consumers.
2. Employment Data:
- Nonfarm Payrolls: This report measures the change in the number of jobs created or lost in the nonfarm sector of the economy.
- Unemployment Rate: This indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking work.
- Average Hourly Earnings: This reflects the average wage growth for non-supervisory workers in the private sector.
3. Manufacturing Data:
- Institute for Supply Management (ISM) Manufacturing Index: This measures the health of the manufacturing sector based on surveys of purchasing managers.
- Durable Goods Orders: This report tracks orders for manufactured goods that are expected to last at least three years.
- Factory Orders: This provides a broader view of manufacturing activity, encompassing both durable and non-durable goods.
4. Interest Rate Decisions:
- Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Meetings: The FOMC, the policymaking body of the Federal Reserve, meets regularly to set interest rate targets and discuss monetary policy.
- Central Bank Announcements: Central banks around the world, such as the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of England (BOE), announce their interest rate decisions and policy stances.
5. Other Key Indicators:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country.
- Retail Sales: This tracks the total value of sales at retail stores, providing insight into consumer spending.
- Housing Starts: This indicates the number of new homes being built, reflecting the health of the housing market.
Understanding the Impact: How Economic Data Moves the Market
Economic data releases can have a significant impact on the stock market. Positive data, such as strong job growth or low inflation, generally boosts investor confidence, leading to higher stock prices. Conversely, negative data, such as weak economic growth or rising inflation, can trigger market sell-offs.
The reaction to economic data can vary depending on several factors:
- Magnitude of the release: Larger deviations from expectations can lead to more pronounced market reactions.
- Market sentiment: Existing market conditions and investor expectations play a significant role in shaping the response to data releases.
- Policy implications: Data releases can influence the decisions of central banks, impacting interest rates and other policy measures.
The Importance of the Economic Calendar: A Tool for Informed Decision-Making
The economic calendar provides investors with a valuable framework for understanding the market’s potential movements. By tracking upcoming data releases, investors can:
- Anticipate potential market volatility: Knowing when key data points are due can help investors prepare for potential market swings.
- Identify trading opportunities: Data releases can create short-term trading opportunities based on market reactions.
- Assess the health of the economy: The economic calendar provides a comprehensive view of the economy’s performance, enabling investors to make informed decisions.
Navigating the Economic Calendar: Tips for Effective Use
- Focus on key data points: Prioritize tracking the most impactful data releases, such as inflation reports, employment figures, and interest rate decisions.
- Understand market expectations: Pay attention to analysts’ forecasts and market consensus for upcoming data releases.
- Monitor reactions: Observe the market’s immediate response to data releases and assess its potential impact on future trading.
- Stay informed: Regularly consult reputable sources, such as financial news outlets and economic research firms, for analysis and insights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Economic Calendar
1. Where can I find a reliable economic calendar?
Numerous financial websites and data providers offer comprehensive economic calendars. Some popular options include:
- Investing.com: https://www.investing.com/economic-calendar/
- Trading Economics: https://tradingeconomics.com/calendar
- Bloomberg: https://www.bloomberg.com/markets/economic-calendar
2. How often is the economic calendar updated?
Economic calendars are typically updated on a daily basis, reflecting changes in release dates, times, and revisions to data.
3. How can I interpret the data releases on the economic calendar?
Pay attention to the following:
- Actual vs. Expected: Compare the actual data release to the market’s expectations.
- Previous Release: Consider how the current release compares to the previous data point.
- Historical Context: Analyze the data in the context of historical trends and economic cycles.
4. Is the economic calendar a foolproof guide to market movements?
No, the economic calendar should not be considered a definitive predictor of market behavior. Other factors, such as geopolitical events and company-specific news, can also influence market direction.
5. How can I use the economic calendar to enhance my investment strategy?
The economic calendar can be a valuable tool for:
- Timing trades: Identify potential trading opportunities based on expected market reactions to data releases.
- Managing risk: Adjust portfolio positions based on the potential impact of upcoming data releases.
- Evaluating economic trends: Gain insights into the overall health of the economy and its implications for investment decisions.
Conclusion: The Economic Calendar – A Vital Compass for Investors
The economic calendar serves as a crucial compass for navigating the complexities of the stock market. By providing a comprehensive overview of upcoming economic data releases, it empowers investors to anticipate potential market movements, identify trading opportunities, and make informed investment decisions. While the economic calendar should not be relied upon as a sole predictor of market behavior, it remains an invaluable tool for understanding the forces that shape the market landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Market: Understanding the Economic Calendar. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!